In today's fast-paced world, high-speed connections have become vital for companies across industries. With the level of automation rising, the need for reliable and efficient data monitoring structures has never been more critical. Enter 5G, the fifth-generation wireless technology, which has captured the spotlight in machine-type communication and the Internet of Things (IoT).
With its unparalleled reliability, reduced latency, and increased device capacity, private 5G holds the promise of transforming industries. It has the potential to greatly enhance use cases from smart logistics to remote control, monitoring of assets and predictive maintenance. Considering its fit with the needs of industrial players, we see especially bright futures for applications in equipment manufacturing, petrochemical & pharmaceutical, ports, automotive and domestic appliances.
Industrial 5G in China - A Promising Path to Success
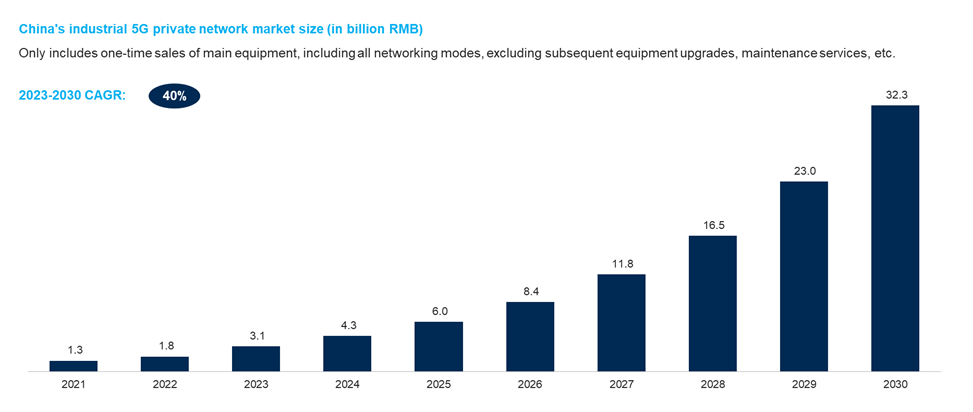
Source: IoT ONE market size prediction (based on project data from China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom, expert interviews, and cross-analysis of third-party market research reports)
In China, a frontrunner in 5G adoption, the industrial 5G private network market has seen rapid growth since its initial rollout. Projections indicate that the Chinese market is poised to witness over 6,000 new projects this year alone. The 5G networking equipment part of the market alone is expected to reach a staggering 6 billion RMB by 2025, with potential to exceed 32 billion RMB by 2030. When considering end-to-end support (including design, setup, cloud services, software, maintenance, etc.), the market size will even be well over ten times as large, signifying the immense value of industrial 5G.
At the core of China’s industrial 5G market growth, we identify the following drivers:
- Demonstration effect of pilot projects: Successful pilot projects by leading enterprises will inspire wider commercial applications, driving market expansion. With thousands of projects each year, it might be only a matter of time before 5G becomes the standard.
- Enhanced policy support: Strong backing from national policies and operators will accelerate industrial 5G market development.
- Product price decline: Declining 5G product costs will open opportunities for broader adoption, especially among smaller businesses.
- Terminal product upgrade: Advancements in terminal products will unlock the full potential of private 5G networks.
However, market development isn’t without obstacles as the following challenges could inhibit growth to a certain extent:
- Industry cycle limitations: High costs may slow down the market's growth, considering average equipment turnover within industries.
- 6G technology substitution: Anticipating 6G pilots kicking off in 2030, part of companies might be prompt to delaying 5G adoption until they assess the benefits of the newer technology.
- Policy subsidies retreat: A swift reduction in policy support could hinder further investments in private 5G networks.
Considering both drivers and challenges, the outlook for private industrial 5G in China remains promising. With an unwavering commitment from the government to support industry development, an explosively growing number of projects and a robust ecosystem of local players, China is well-equipped to support industry growth in the short to medium term.
Who Leads China's Private 5G Market?
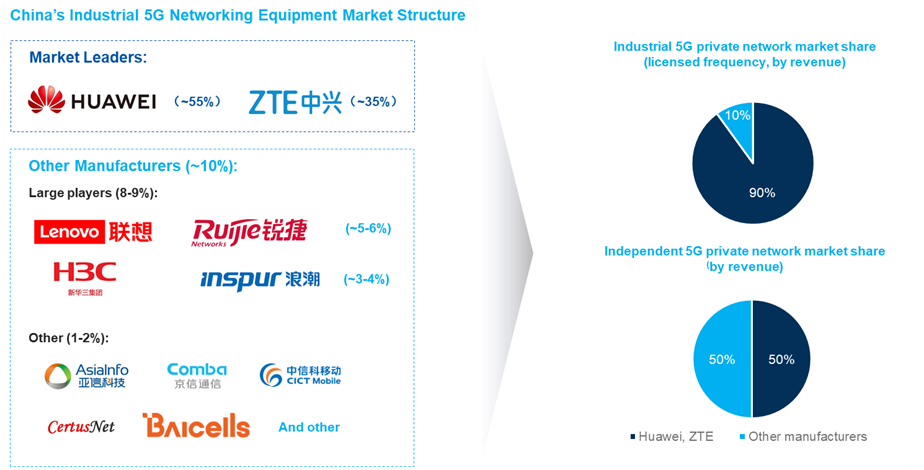
Source:IoT ONE market share estimation based on expert interview data
Currently, the Chinese market for licensed private 5G networks is heavily concentrated, with Huawei and ZTE accounting for over 90% of market share. While they lead the charge in large-scale projects, a deeper look reveals that the majority are actually small to medium-sized projects. Looking at this part of the market, and especially the independent 5G private network market (where network hardware is fully owned by the customer) the landscape shifts dramatically. Here, other players claim a larger slice of the pie, leveraging industry-specific advantages and significant price differences to carve their niche.
Noticeably, prominent players are all domestic Chinese companies. While foreign companies face no explicit barriers to entry, Chinese network operators exhibit a clear preference for local partners. Consequently, foreign players predominantly serve industrial companies from abroad who are unable to utilize Chinese equipment for political reasons, leaving them with a relatively smaller market share.
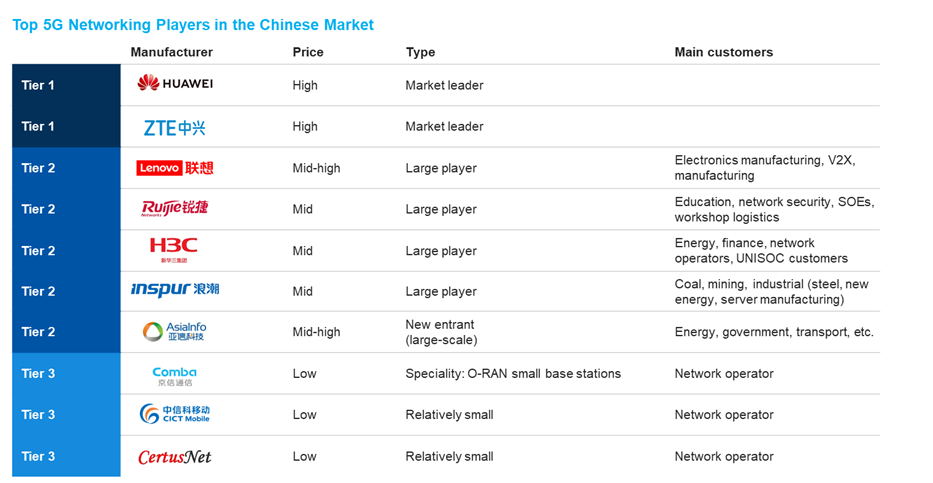
Source: IoT ONE analysis
Venturing into the overall market terrain, networking equipment companies can be categorized into three tiers. Tier 1 comprises market leaders Huawei and ZTE, paving the way.
Tier 2 sees formidable players Lenovo, Ruijie, H3C, Inspur and AsiaInfo. Distinguished by their sales teams dedicated to specific focus industries, they gain a competitive edge through their unique backgrounds. IT powerhouses Inspur and Lenovo boast exceptional enhanced integration service capabilities, while communication experts H3C and Ruijie possess unparalleled networking knowledge, pinpointing precisely where within processes 5G can deliver the greatest advantages.
Lastly, tier 3 players, smaller in scale, include players like Comba, CICT Mobile and CertusNet. Relying primarily on their network operator relationships, they are positioned as valuable additions to projects, showcasing strengths in specific equipment domains and competing at a more accessible price point, rather than offering their expertise in end-to-end projects.
What About Unlicensed 5G?
Despite gaining momentum worldwide, unlicensed 5G faces significant obstacles in China, where 'real' unlicensed 5G is yet to emerge. Currently, projects labeled as unlicensed 5G private networks in China utilize LTE-U technology, which lacks the full capabilities of true 5G. The road to unlicensed 5G's success hinges on several crucial factors. Overcome the technological constraints, explore operators' preferences, and understand the role of state support to unlock the full potential of unlicensed 5G in China's market.
First and foremost, technological constraints pose a formidable barrier. Power limitations have been imposed on unlicensed 5G, restricting its ability to effectively cover vast distances. Should these restrictions be lifted, unlicensed 5G equipment could potentially outperform licensed 5G alternatives. However, until this issue is resolved, the full potential of unlicensed 5G remains untapped.
Compounding the challenge, operators' deployment preferences present further hurdles. Chinese operators currently favor virtual and hybrid private networks over independent private networks, which impacts the adoption of independent unlicensed 5G, or in this case LTE-U networks. After all, virtual and hybrid networks use more of operator networking infrastructure, meaning generated revenue is significantly larger. At present, LTE-U is mainly adopted by private small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in industries such as mining, coal, and education who seek to improve efficiency and safety while retaining a high degree of control over their networks.
Equally crucial is state support for unlicensed 5G to thrive. The influential relationship with operators in the licensed spectrum market nudges established 5G networking players away from investing in 5G-U technology to safeguard their existing business ties. What this means is that it is hard for unlicensed 5G to develop both with and without direct cooperation with network operators. To have a chance at flourishing in China's market, a clear and decisive state-driven push is critical to change the status quo and pave the way for 5G-U investment.
Automation and 5G: the Future of Industrial Connectivity?

Source: IoT ONE analysis
Leading automation players, such as Siemens, Schneider Electric, Rockwell, Bosch, and ABB, are strategically navigating the path of 5G adoption. While the potential of 5G is undeniable, its true value lies in practical applications. They recognize that 5G isn't the sole contender, as Wi-Fi 6, a more mature technology, can deliver comparable benefits across many use cases. The key, however, lies in uncovering the niche areas where 5G emerges as a game-changer, setting itself apart from the competition.
Laser-focused on delivering excellence to their clients, market leaders are focused on guaranteeing their product offerings perform ultimately regardless of whether their customers use 5G or not. Siemens stands at the forefront, already introducing its 5G networking products, displaying an unwavering belief in 5G's potential. However, this journey isn't merely about offering 5G solutions; it's about proving its worth in real-world scenarios.
The technological frontier of 5G is teeming with exciting use cases, and the groundwork is being laid. Bosch, a trailblazer, leverages 5G's prowess in their automotive component factory, unlocking potential in Edge Cloud AGV, digital twin applications for online diagnosis and predictive maintenance, and AI AOI visual inspections. Meanwhile, Schneider Electric's commitment is evident, having embraced 5G-powered flexible production lines. This enables high-variety, small-batch manufacturing, delivering substantial benefits in terms of operational efficiency and cost optimization. Currently leveraging 5G to optimize their own operations, they are bound to offer valuable use cases to their customers in the future as well.
Embracing the spirit of collaboration, Schneider Electric has already joined forces with Gemini and Qualcomm to launch the industry's first 5G solution for crane control system automation. These ventures exemplify how 5G is steadily revolutionizing industries and is already finding customers in industries like ports and steel, setting the stage for transformative change.
What's next?
As the industrial 5G landscape continues to evolve, the question remains: will 5G become the dominant networking technology in China's industrial automation market? With its transformative potential, the future of 5G seems promising, but its widespread adoption hinges on various factors. As businesses look to leverage the power of 5G for their facilities or explore opportunities in the 5G space, the potential for growth and innovation in China's industrial landscape is vast. Embrace the possibilities and stay ahead of the curve in this dynamic era of connectivity.
Are you ready to unlock the full potential of 5G in your facilities or venture into the dynamic world of 5G solutions? Our team is here to guide you through the ever-evolving landscape of industrial connectivity. Whether you seek to revolutionize your operations or explore new horizons, we are dedicated to helping your business seize the boundless opportunities that 5G has to offer.




