This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the policy environment, domestic market, investment and financing status, and application use cases for digital twins in several vertical industries. A digital twin is an integrated solution that utilizes physical models, sensor updates, operational history, and other data to integrate multi-disciplinary and multi-probability simulation processes to complete mapping in a virtual space. The aim is to reflect the entire life cycle of the corresponding entity equipment or asset. A digital twin can thus be seen as a digital mapping system of one or more interdependent systems.
In recent years, digital twin technology has been widely used in manufacturing, smart cities, healthcare, and other fields. Even the currently trending metaverse is a process of digitization reaching a certain depth of integration between the real world and the virtual world.
China has long laid out relevant policies for digital twins. With the release of the "14th Five-Year Plan," the deployment and implementation of digital twin-related policies have accelerated significantly in recent years, providing a favorable environment for the industry and further enhancing the standardization of its development.
Investing in Digital Twins
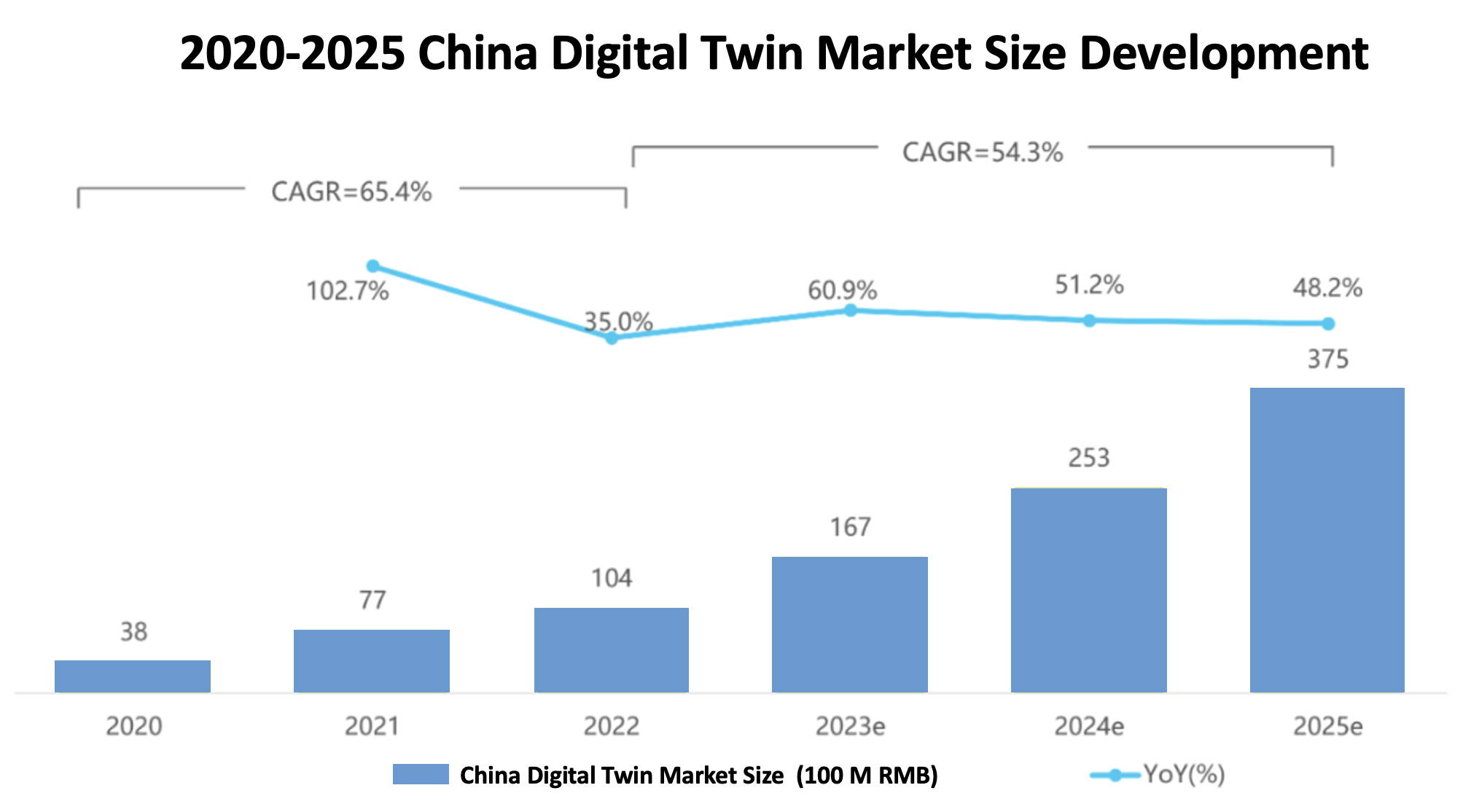
China's digital twin market exceeded 10 billion yuan ($1.4 billion) in 2022 after a period of vigorous development. According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology and the World Economic Forum, as of 2021, the global digital twin market size reached $4.9 billion. It is expected that the global digital twin market will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 58%, reaching $48 billion by 2026. China's digital twin market grew at a CAGR of 65% from 2020 to 2022.
With the advancement of digital transformation across industries, the penetration rate of digital twins will rapidly increase, driving the future growth of the domestic digital twin market. It is expected that the domestic market size will reach 37.5 billion yuan ($5.1 billion) by 2025, with a CAGR of 54%.
Before 2014, around 30 newly added digital twin-related companies were added to China's market landscape each year. From 2015 to 2018, that number increased to a rate of 50 to 60 per year. From 2019 to 2021, the number of new companies accelerated to more than 100 before peaking in the near term. This indicates that China's market players are continuously growing, with many latecomers, multiple market opportunities, and great market potential. Currently, the main players in the industry are in the fields of geographic information, new surveying and mapping, game engines, digital modeling, and visualization. With the emergence of new engines and new bases for urban digital twins, many companies specializing in artificial intelligence, big data, simulation, and computing services will enter in the future.
Players in the digital twin industry can be divided into two categories: digital twin-related technology providers and solution integrators. Technology providers include visualization vendors, BIM, GIS, CIM, and CAD/CAE simulation modeling technology vendors. Solution providers provide customized IoT solutions and services to customers in different industries, helping them achieve advanced levels of digital twin solutions. The Internet giants (BAT), Huawei and other cloud vendors are all in the market, as well as the three major telco operators, Wanrui Technology, ThoughtWorks, and other vendors in vertical fields.
Financing enthusiasm is gradually returning after a slow 2022. According to IT Orange data, from 2017 to 2022, there were a total of 80 financing events for Chinese digital twin-related companies, with a total financing amount of 8.3 billion yuan. Financing in 2022 alone reached 2.5 billion yuan. A-rounds and earlier events remain dominant, but strategic investments and pre-IPO events have become more frequent in recent years. In terms of application scenarios, cities are the most important landing scenario for digital twins, followed by manufacturing.
Empowering Industries with Digital Twins
Smart Cities: Digital twin cities combine the virtual and the real in top-level design, overlapping physical entities with their corresponding twin models based on digitization and informatization. The goal is to achieve interaction between the virtual and the real to improve the effectiveness of planning, operations, and maintenance in areas such as transportation networks, utilities, and urban emergencies.
Smart Industrial Parks: Digital twins empower reductions in industrial park carbon emissions. Data is collected through sensors and combined with AI algorithms to support carbon emission planning, carbon calculation, energy efficiency monitoring, and operations optimization, with the goal of achieving the carbon targets of industrial parks.
Manufacturing: Industrial enterprises are investing heavily in the Internet of Things and edge computing to enable digital twin technology to complete tasks such as production optimization, energy consumption tracking, equipment maintenance planning, product design, and supply chain management. There are ultimately four values in focus: improving quality, reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and minimizing risk.
Medical Management: Digital twin technology collects and calculates diverse and multidimensional data from medical equipment and medical information systems to enable AI modeling. Combined with BIM, CIM, and other technologies, the physical space of a hospital can be mapped into a digital twin model. This model helps to achieve fine management of medical work, outpatient management, and equipment management through functions such as prediction and analysis.
Transportation: In conjunction with efforts by cities, regional governments are combining traffic information data and high-precision maps to create smart transportation systems that can be simulated in real-time to predict traffic behavior and improve efficiencies and safety.
.png)
Vehicle Testing: Real-time vehicle data is collected and transmitted to the digital twin platform, which enables the evaluation of vehicle behavior under diverse situations. The car can then make decisions based on its own algorithm, such as how to operate on an icy road. The construction of virtual vehicle models also simplifies the setup of testing scenarios, thereby improving the efficiency of autonomous driving testing.
Digital twins are complex systems that involve multiple stages of engineering, diverse fields of expertise, and collaboration across corporate departments. Collaboration across various industries is also critical to technical innovation and often to the success of deployments. By building a collaborative digital twin industry ecosystem that promotes open-source innovation, China is seeking to drive the application of digital twin technology into more industries, advance technological development, and accelerate the digital transformation of the economy as a whole.
These efforts are being made under the backdrop of increased emphasis on technological independence and digital security in various industries of the Chinese economy.




