下载PDF
University of Utah Health strengthens referring partner relationships
技术
- 功能应用 - 企业资源规划系统 (ERP)
- 应用基础设施与中间件 - 数据交换与集成
适用行业
- 医疗保健和医院
适用功能
- 商业运营
- 质量保证
用例
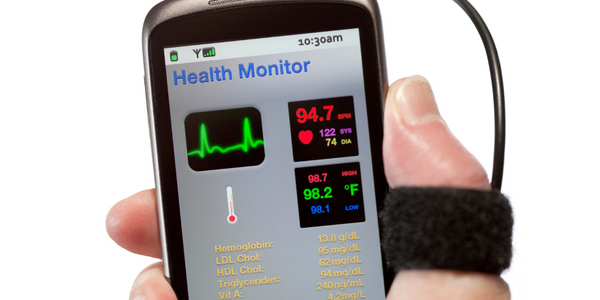
- 远程病人监护
- 监管合规监控
- 远程协作
服务
- 系统集成
- 数据科学服务
挑战
As a tertiary medical center in a five-state referral area encompassing more than 10 percent of the continental United States, University of Utah Health has long been committed to building strategic alliances with referring physicians. Yet one unwelcome perception persisted. A lag in the consistency of patient follow-up often resulted in a lack of uniformity of care and a breakdown in efficient communications with physicians. The reason for the lag was that University of Utah Health often had to verify disparate and sometimes inaccurate provider discharge data. Two to three FTEs dedicated substantial time to sorting through and manually validating accurate provider names, locations, credentials and more every day, using MPI, Google and other publicly available resources. As a result of this time-consuming verification process, referring providers were left in the dark on treatments, interventions and medications conducted on behalf of their patients, which, in the worst of situations, led to redundancies in after-discharge treatment, and increasing frustration among referring providers.
关于客户
University of Utah Health, the Mountain West’s only academic healthcare system, is staffed by more than 1,000 board-certified physicians trained in over 200 medical specialties and receives thousands of patient referrals each year in a five-state area. Facilitating seamless, secure patient transitions was crucially important, but without a means to promote accuracy and completeness of the provider directory, there were often breakdowns in communications with referring physicians. In an effort to elevate the all-important partnership between the medical center and physicians, the medical center leveraged LexisNexis® Provider Data MasterFile™ last year. Since choosing the comprehensive data solution, the medical center has witnessed a surge in satisfaction among physicians and patients, improved accuracy and efficiency, the elimination of redundancies and significant time and cost savings.
解决方案
University of Utah Health chose LexisNexis® Provider Data MasterFile™ to meet its goals of transitioning patients more efficiently and helping themselves and their referring partners meet Meaningful Use (MU) Transitions of Care objectives. These MU objectives state that Eligible Hospitals and Eligible Providers who transition their patients to another setting or provider of care, or who refer their patients, should provide a summary care record for targeted percentages of their patients. By linking the Provider Data MasterFile with its current Epic electronic hospital record (EHR) system, University of Utah Health was able to significantly improve the accuracy of provider data, which can change by as much as 25 percent in a single year. The powerful Provider Data MasterFile solution provides deep data coverage of more than 8.5 million U.S. health practitioners, with drill-down attributes such as name integrity (individual names, DBAs and Formerly Known As), addresses across all practice locations, billing locations, updated key data information, state license(s) and other credentials. The Provider Data MasterFile is continuously updated with billions of data points on every healthcare provider in the nation. As a result, University of Utah Health has made great strides in enhancing the care transition and strengthening its referrer alliances. On the front end, the patient’s physician information is entered into the Epic EPR provider dictionary. The data is then bumped against the Provider Data MasterFile and in nearly three-quarters of these instances, a match is provided with an 85 percent or higher accuracy rate. Now that verification isn’t forced to go through multiple people, the updated data is back in the system immediately, and the process has sped up significantly.
运营影响
数量效益
相关案例.

Case Study
Hospital Inventory Management
The hospital supply chain team is responsible for ensuring that the right medical supplies are readily available to clinicians when and where needed, and to do so in the most efficient manner possible. However, many of the systems and processes in use at the cancer center for supply chain management were not best suited to support these goals. Barcoding technology, a commonly used method for inventory management of medical supplies, is labor intensive, time consuming, does not provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and can be prone to error. Consequently, the lack of accurate and real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple supply rooms in multiple hospital facilities creates additional inefficiency in the system causing over-ordering, hoarding, and wasted supplies. Other sources of waste and cost were also identified as candidates for improvement. Existing systems and processes did not provide adequate security for high-cost inventory within the hospital, which was another driver of cost. A lack of visibility into expiration dates for supplies resulted in supplies being wasted due to past expiry dates. Storage of supplies was also a key consideration given the location of the cancer center’s facilities in a dense urban setting, where space is always at a premium. In order to address the challenges outlined above, the hospital sought a solution that would provide real-time inventory information with high levels of accuracy, reduce the level of manual effort required and enable data driven decision making to ensure that the right supplies were readily available to clinicians in the right location at the right time.

Case Study
Gas Pipeline Monitoring System for Hospitals
This system integrator focuses on providing centralized gas pipeline monitoring systems for hospitals. The service they provide makes it possible for hospitals to reduce both maintenance and labor costs. Since hospitals may not have an existing network suitable for this type of system, GPRS communication provides an easy and ready-to-use solution for remote, distributed monitoring systems System Requirements - GPRS communication - Seamless connection with SCADA software - Simple, front-end control capability - Expandable I/O channels - Combine AI, DI, and DO channels
Case Study
Driving Digital Transformations for Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices
Diagnostic devices play a vital role in helping to improve healthcare delivery. In fact, an estimated 60 percent of the world’s medical decisions are made with support from in vitrodiagnostics (IVD) solutions, such as those provided by Roche Diagnostics, an industry leader. As the demand for medical diagnostic services grows rapidly in hospitals and clinics across China, so does the market for IVD solutions. In addition, the typically high cost of these diagnostic devices means that comprehensive post-sales services are needed. Wanteed to improve three portions of thr IVD:1. Remotely monitor and manage IVD devices as fixed assets.2. Optimizing device availability with predictive maintenance.3. Recommending the best IVD solution for a customer’s needs.

Case Study
HaemoCloud Global Blood Management System
1) Deliver a connected digital product system to protect and increase the differentiated value of Haemonetics blood and plasma solutions. 2) Improve patient outcomes by increasing the efficiency of blood supply flows. 3) Navigate and satisfy a complex web of global regulatory compliance requirements. 4) Reduce costly and labor-intensive maintenance procedures.

Case Study
Harnessing real-time data to give a holistic picture of patient health
Every day, vast quantities of data are collected about patients as they pass through health service organizations—from operational data such as treatment history and medications to physiological data captured by medical devices. The insights hidden within this treasure trove of data can be used to support more personalized treatments, more accurate diagnosis and more advanced preparative care. But since the information is generated faster than most organizations can consume it, unlocking the power of this big data can be a struggle. This type of predictive approach not only improves patient care—it also helps to reduce costs, because in the healthcare industry, prevention is almost always more cost-effective than treatment. However, collecting, analyzing and presenting these data-streams in a way that clinicians can easily understand can pose a significant technical challenge.