Download PDF
Faraone's Innovative Approach to Architectural Component Design with IoT
Technology Category
- Analytics & Modeling - Digital Twin / Simulation
- Sensors - Utility Meters
Applicable Industries
- Glass
- Life Sciences
Applicable Functions
- Product Research & Development
- Quality Assurance
Use Cases
- Time Sensitive Networking
- Virtual Reality
Services
- Testing & Certification
The Challenge
Faraone SRL, an Italian provider of architectural components, was faced with the challenge of designing a new full glass balustrade with a special aluminum profile at the bottom to hold the glass structure in place. The goal was to save on development time, material, and production costs, while increasing the stiffness of the aluminum profile. The development engineers at Faraone needed a new design strategy and special optimization tools to help reach these goals. The design of architectural components such as a balustrade can be challenging, since the design does not only have to look good, it also has to meet several safety requirements and standards. In addition, all designs have to be developed within the shortest time possible. To meet these challenges the engineers, architects and designers at Faraone are always looking for solutions that can reduce their design and testing cycles.
About The Customer
Faraone SRL is an Italian provider of architectural components. The company is committed to continuously investing in state-of-the-art analysis tools, technology research and the development of new, innovative products. Design plays a fundamental role in all new Faraone products and designers and engineers work in teams to find the smarter solutions for every new product. The company is known for its commitment to quality and innovation, and its ability to meet the challenging demands of the architectural industry. Faraone's recent project involved the design of a new full glass balustrade with a special aluminum profile at the bottom to hold the glass structure in place.
The Solution
Faraone found their solution with solidThinking Inspire, a design software that allows for structural optimization and validation in one platform. The engineering team started from zero and used simulation and optimization to drive the design. They first created a simple profile and used it to perform a topology optimization of the profile in solidThinking Inspire. The optimization results inspired the final design, which was refined by the design team, and lastly validated in solidThinking Inspire. A typical optimization process follows these steps: Creation of the design space and application of loads and boundary conditions. The optimization tool uses the input to propose an optimal structure. The design proposal offers the best possible combination of lightweight and structural efficiency. Subsequently, the part is quickly refined to define the final shape, which is then again analyzed with Inspire to verify its structural performance.
Operational Impact
Quantitative Benefit
Related Case Studies.
Case Study
Corporate Identity Solution Adds Convenience to Beckman Coulter
Beckman Coulter wanted to implement a single factor solution for physical and remote logical access to corporate network. Bechman Coulter's users were carrying smart card badges for doors, but also needed a one-time password token to access to our corporate network when they were not in the office. They wanted to simplify the process.

Case Study
Embracing Business Success in Real Time
· Increase control over growing Big Data to improve business decisions · Manage data for 28,000 biotechnology stockkeeping units in the fields of microbiology, molecular biology, animal cell cultures, plant tissue cultures, and lab ware for laboratory chemicals · Accelerate report generation and analysis with real-time data
.png)
Case Study
Discrete Manufacturing Industries (Fiberglass Pipe)
The implementation of ERP software in a Discrete Manufacturing organization needs to be strategic, irrespective of its size and capacity. The client had already implemented an ERP system which fulfilled their requirements but was not efficient enough. Efficiency here meant Synchronized Planning, Updating and Multisite Planning. Planning at client’s place was done outside the ERP system. Lack of proper synchronization to the ERP system paved way to huge delays in the changes getting updated in the system. These delays caused disruption in achieving delivery schedules. Multisite Planning is a solution to an organization which has multiple production units (may or may not be geographically separated) and thus needs planning across these units to synchronize production activities within them. The client also has multiple factories and hence Production Planning control is very essential in their case. Since Multisite planning was not possible with Baan ERP system, this was another bottleneck for the client.
Case Study
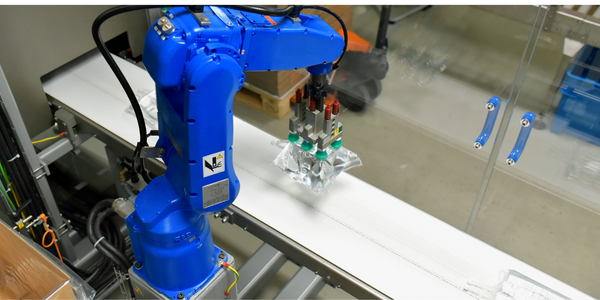
Flow Robotics: Scaling Up Production and Accelerating Product Development with IoT
Flow Robotics, a Danish manufacturer, developed flowbot™ ONE pipetting robots to alleviate the strain on bioanalysts in life-science laboratories and hospitals across Europe. These robots were designed to automate part of the testing process, speeding up the time it takes to produce results and reducing pressure on staff. However, the company faced challenges in scaling up production and accelerating product development. High workloads and physically challenging conditions have long been an issue for laboratory professionals. Flow Robotics estimates that around half of medical lab technicians carry out the same arm movements for at least a quarter of their working day. The American Society for Clinical Pathology reported that 85% of laboratory professionals feel burnt out; 36% struggle with inadequate staffing; and 32% face a heavy workload and pressure to complete all testing on time.

Case Study
Asia Airfreight Terminal Enhances Operational Efficiency with CommScope's RUCKUS Solutions
Asia Airfreight Terminal (AAT), a leading cargo handling company based out of Hong Kong International Airport, was facing challenges with its Wi-Fi network, which was critical for the functioning of its automated Material Handling System (MHS) within the warehouse. Any interference or lost signals could directly impact their operational efficiency. AAT also had separate networks for their office and CCTV cameras, which made the job of their data center challenging. The company was in search of a Wi-Fi network configuration that could streamline their networks and reduce its network management workload. AAT was already running on equipment from a competing vendor, and the new solution needed to prove its worth in scalability and reliability.

Case Study
High Density Stacking Capability Enhances Productivity in 3D Part Production at Decathlon
Decathlon, the world’s largest sporting goods retailer, was faced with a mold injection problem on a small component for shooting glasses that connects the frame to the lenses. The company was seeking a solution that would avoid the expense of tooling and increase efficiency in production. They decided to test the new 3D stacking solution developed by 3D Systems to evaluate additive manufacturing for production. After conducting a feasibility study on the Figure 4 solution and stacking feature, Decathlon’s teams confirmed the productivity and economics of additive manufacturing and decided that this solution could be considered for batch-run production of the final product.





