Download PDF
Process Redesign in Cloud-Based Software Company Saves $2M

Technology Category
- Sensors - Flow Meters
- Sensors - Liquid Detection Sensors
Use Cases
- Augmented Reality
- Mixed Reality
The Challenge
A leading cloud-based software company was facing difficulties in achieving the desired efficiencies and scale needed to support consistent growth in terms of accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) functions from its facilities in South America and Central Europe. The company's previous IT service providers' collections data was consistently low, around 60% based on historical records. This led to a cash flow problem and an increase in the aging of outstanding receivables. The company was also seeking standardization across geographies. To address these issues, the company set a goal of achieving 70% collections and reached out to Cognizant, their strategic partner of seven years, for assistance.
The Customer
Not disclosed
About The Customer
The customer is a leading cloud-based software company with facilities in South America and Central Europe. They were struggling with achieving the desired efficiencies and scale needed to support consistent growth in terms of accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) functions. The company was also facing issues with low collections data, cash flow problems, and an increase in the aging of outstanding receivables. They were seeking to improve these areas and standardize their operations across geographies. The company had a long-standing relationship with Cognizant, their strategic partner of seven years.
The Solution
Cognizant began by conducting an audit of the aging receivables report and performed a detailed analysis of the baseline. They redesigned the end-to-end AR process by establishing standard operating procedures (SOPs) for collections and billing agents. This helped agents identify their goals and achieve measurable targets, improving efficiency and outcomes. Cognizant's data scientists analyzed customer payment patterns, which informed their collections approach, touchpoints, and timeline. They found that 30% of customers pay after a reminder call, so agents began calling immediately after the due date, resulting in quicker payments. Cognizant worked closely with agents to understand and address their challenges. They used the company’s own global CRM platform to mirror the processes between the company and its customers. Cognizant also streamlined the company’s operations and call center to reduce language barriers and service disruptions and to acquire highly skilled resources.
Operational Impact
Quantitative Benefit
Related Case Studies.

Case Study
KSP Steel Decentralized Control Room
While on-site in Pavlodar, Kazakhstan, the DAQRI team of Business Development and Solutions Architecture personnel worked closely with KSP Steel’s production leadership to understand the steel production process, operational challenges, and worker pain points.

Case Study
How ScopeAR's Technology Helped Increase Efficiency by 30%
Scope AR collaborated with one of their large industrial clients to perform a side-byside comparison of Scope AR’s WorkLink software, an Augmented Reality software, versus using traditional paperbased methods to create manufacturing instructions. The client chose a complex assembly process for a proprietary spring-loaded hatch.The assembly process contained over thirty steps that involved things such as fitting components at specific angles to ensure proper assembly, screwing down different screw types in correct locations, and grabbing parts that had similar exteriors.The client chose this assembly process because it contained common steps that are frequently used in other processes as well as unique steps that are confusing and if done wrong would cause severe quality issues.

Case Study
Boeing Cuts Production Time by 25% with Skylight on Glass
130 miles of wiring go into every new Boeing 747-8 Freighter, tucked away overhead and underfoot from the cockpit to the wheel wells.Every Boeing aircraft, from the workhorse 737 to the new 787 Dreamliner, has multiple configurations, each with its own wiring scheme. In past years, technicians used “phone books” full of diagrams to do their work. Even with laptops, the same basic problem arised: constant look-away interruptions as workers got directions and cross-checked diagrams and schematics.

Case Study
AGCO is Increasing the Efficiency of its Manufacturing Programs Using Glass
The thorough inspection of a finished product is an essential step in the quality-control process. In the beginning, quality checklists were accessed using paper on clipboards. As technology improved, computers were utilized. But computers required additional time to access, and couldn’t be carried to the equipment being inspected. Tablets replaced computers, but were easily broken and expensive to replace.
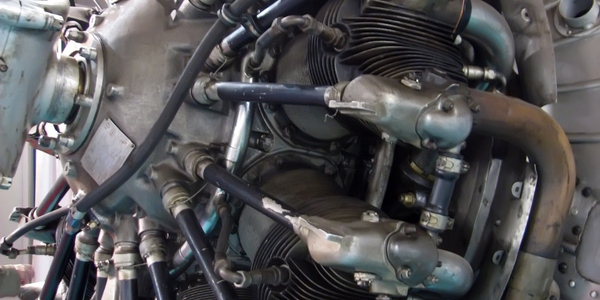
Case Study
Getting the Torque Just Right Could Save Millions for Aerospace Companies
GE Aviation loses millions of dollars each year to errors made at key points during the assembly and overhaul of its engines. The costs show up in lost productivity, delays in testing, delays in customer deliveries, and the man-hours required to troubleshoot and correct faults. If errors arenʼt detected until after the engines are sent to customers, the repair costs exponentially increase.B-nuts are one such key manufacturing point. They play a critical role in aircraft engine fluid lines and hoses, providing a sturdy, reliable seal―but only if tightened and torqued properly. If not torqued properly, there will be a need for a maintenance do-over, cancelled flight, or even an in-flight shut down.






